What is CORS ?
Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) is an HTTP-header based mechanism that allows a server to indicate any other origins (domain, scheme, or port) than its own from which a browser should permit loading of resources. CORS also relies on a mechanism by which browsers make a “preflight” request to the server hosting the cross-origin resource, in order to check that the server will permit the actual request. In that preflight, the browser sends headers that indicate the HTTP method and headers that will be used in the actual request.
When browser throws CORS error?
CORS is a security mechanism built into modern web browsers. It basically blocks all the HTTP requests from your front end to any API that is not in the same “Origin” (domain, protocol, and port—which is the case most of the time).
Resolution :
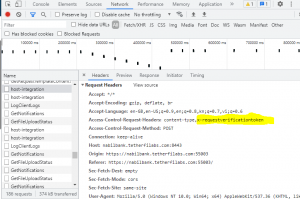
Inspect the error in the web browser console for which the CORS error has been highlighted. Identify the Access-Control-Request-Headers in the browser network console, add CORS filters in web.xml of the respective tomcat app (Ex: C:\Program Files\Apache Software Foundation\Tomcat 9.0\webapps\tetherfi-generic-webservice-interface\WEB-INF\web.xml).
Make sure the following tags
- "cors.allowed.headers" has all the HTTP access control request and custom headers (ex: Content-Type,X-Requested-With,accept,Origin,Access-Control-Request-Method,Access-Control-Request-Headers,X-RequestVerificationToken).
- "cors.allowed.origins" has request origin (ex: https://bank.domain.com:8443).
- cors.exposed.headers has exposed headers (ex: Access-Control-Allow-Origin).
Below is the sample web.xml for reference,
<display-name>Tetherfi Generic Web Service Interface Application</display-name>
<filter>
<filter-name>CorsFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.apache.catalina.filters.CorsFilter</filter-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>cors.allowed.origins</param-name>
<param-value>https://nabilbank.tetherfilabs.com:55003</param-value>
</init-param>
<init-param>
<param-name>cors.allowed.methods</param-name>
<param-value>GET,POST,HEAD,OPTIONS,PUT</param-value>
</init-param>
<init-param>
<param-name>cors.allowed.headers</param-name>
<param-value>Content-Type,X-Requested-With,accept,Origin,Access-Control-Request-Method,Access-Control-Request-Headers,X-RequestVerificationToken</param-value>
</init-param>
<init-param>
<param-name>cors.exposed.headers</param-name>
<param-value>Access-Control-Allow-Origin</param-value>
</init-param>
<init-param>
<param-name>cors.support.credentials</param-name>
<param-value>true</param-value>
</init-param>
<init-param>
<param-name>cors.preflight.maxage</param-name>
<param-value>10</param-value>
</init-param>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>CorsFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
</web-app>
Note that, CORS may still exist if any headers are missing in "cors.allowed.headers" list.